In today’s digital landscape, data is not just an asset—it’s a target. With growing threats and increasingly complex regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, organizations must ensure sensitive data is properly protected. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through data classification and labeling.
What is Data Classification?
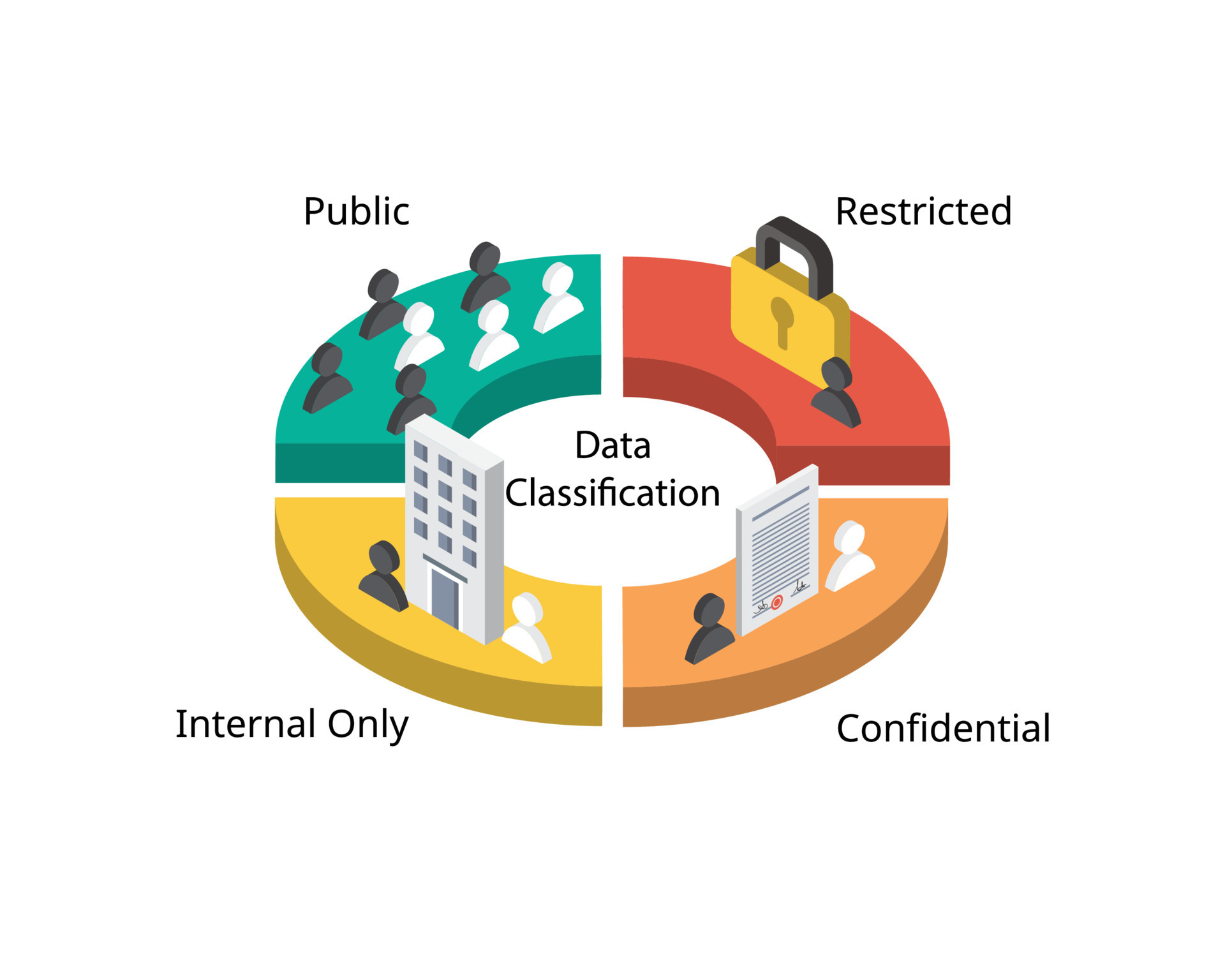
Data classification is the process of categorizing data based on its sensitivity, value, and regulatory requirements. Typically, data is classified into levels such as:
Public – No restrictions; can be freely shared.
Internal – For internal use only; not intended for public distribution.
Confidential – Sensitive data that could cause damage if exposed.
Restricted/Highly Confidential – Data with strict access controls due to legal or strategic reasons.
This classification helps determine how data should be handled, stored, transmitted, and destroyed.
Why is Labeling Important?
While classification defines the category, labeling makes that classification visible and actionable. Labels can be embedded into documents, emails, or files—enabling integrated systems like DLP (Data Loss Prevention) to apply security controls automatically.
For example:
A document labeled “Confidential” can trigger encryption or restrict sharing.
Emails labeled “Internal Use Only” can be blocked from being sent outside the organization.
Benefits for Cybersecurity
Improved Risk Management – By knowing what data is sensitive, organizations can focus resources on protecting what matters most.
Regulatory Compliance – Classification helps meet legal requirements for handling personal or financial data.
User Awareness – Clear labels inform employees how to treat data, reducing accidental leaks.
Automation – Integrated security tools can respond dynamically to labeled data, reducing human error.
How to Implement It?
Start by defining a classification policy tailored to your industry and risk level. Use automated tools that scan, classify, and label data across endpoints, cloud services, and shared drives. Train employees on classification levels and ensure labels are visible and enforced through integrated cybersecurity solutions.
In summary, data classification and labeling are no longer optional—they are foundational pillars of modern cybersecurity. By making data context-aware, organizations can protect their information proactively, reduce breaches, and maintain regulatory confidence.