In today’s data-driven world, organizations are more vulnerable than ever to accidental or intentional data leaks. Whether caused by malicious insiders, human error, or cyberattacks, data breaches can result in significant financial loss, legal penalties, and damage to reputation. This is where Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions become critical.
What Is Data Loss Prevention?
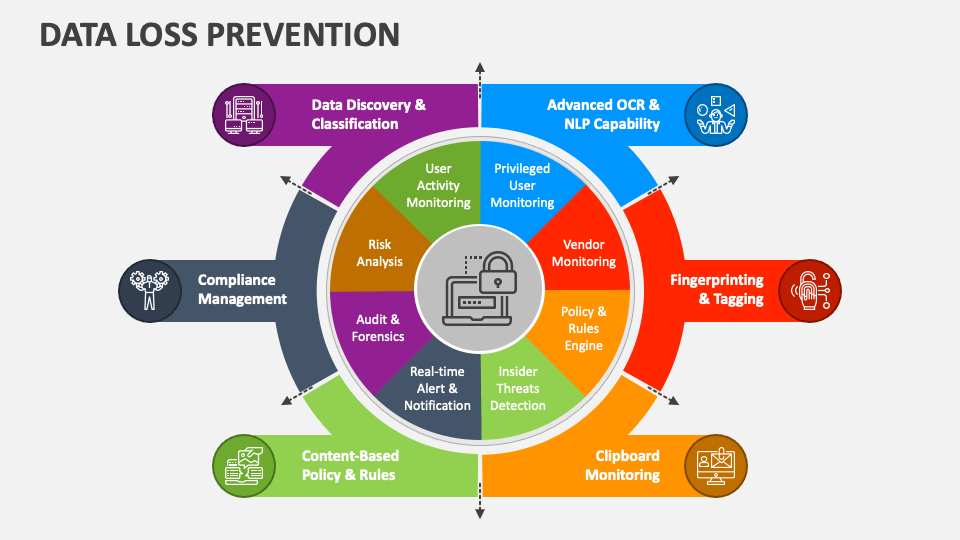
DLP refers to a set of tools and policies designed to detect, monitor, and prevent the unauthorized transmission of sensitive information. It focuses on identifying and controlling data at rest (stored), in motion (being transmitted), and in use (actively accessed).
The goal of a DLP system is to ensure that confidential or critical data does not leave the organization’s control, whether through emails, uploads, USB devices, or cloud sharing.
Why Is DLP Important?
Protects Intellectual Property: DLP solutions help prevent sensitive documents, source code, or trade secrets from being leaked or stolen.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Organizations subject to GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and other regulations must prevent unauthorized access or sharing of protected data.
Mitigates Insider Threats: By monitoring user behavior and flagging anomalies, DLP tools help identify employees who may misuse access.
Supports Data Classification: DLP works hand-in-hand with data classification systems, enforcing different levels of control based on sensitivity.
How Does DLP Work?
DLP solutions operate by combining content inspection, contextual analysis, and policy enforcement:
Content Inspection: Scans files, emails, or messages for sensitive information (e.g., credit card numbers, personal IDs, or keywords).
Contextual Analysis: Evaluates user identity, device type, location, and time to detect unusual behavior or policy violations.
Policy Enforcement: Applies actions like blocking, alerting, encrypting, or quarantining data based on predefined rules.
Types of DLP Solutions
Network DLP – Monitors and controls data in motion across network traffic.
Endpoint DLP – Secures data on user devices, preventing unauthorized transfers via USB, print, or screen capture.
Cloud DLP – Protects data stored or shared in cloud platforms like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, or Dropbox.
Best Practices for DLP Implementation
Start with data classification to identify what needs to be protected.
Develop clear policies that align with business needs and compliance goals.
Educate employees on data handling and DLP alerts.
Continuously monitor and update policies based on evolving risks.
Conclusion
Data Loss Prevention is not just a security tool—it’s a business necessity. As data privacy laws tighten and cyber threats evolve, DLP solutions offer organizations a proactive way to safeguard their most valuable digital assets. When implemented correctly, DLP not only prevents leaks but builds trust with customers, partners, and regulators alike.